|
|
ABCD worldwide audit of
testosterone deficiency in men with type 2 diabetes
ABCD nationwide audit of
testosterone deficiency in men with type 2 diabetes
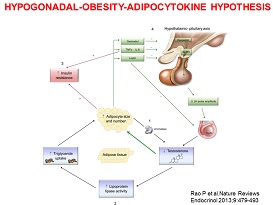
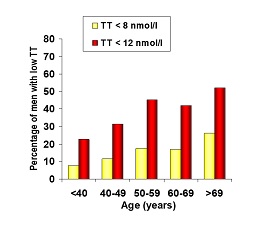
There is a
high prevalence (~40%) of Testosterone Deficiency in men with
Type 2 Diabetes. Testosterone Deficiency is now recognised as a common
co-morbid condition associated with type 2 diabetes.
The ADA Standards
of Medical Care in Diabetes 2021 (Recommendation 4.11) states that ‘In men with diabetes who
have symptoms or signs of hypogonadism such as decreased sexual desire
(libido) or activity, or erectile dysfunction, consider screening with a
morning serum testosterone level’. Male hypogonadism is defined as a
clinical syndrome which must include symptoms with or without signs and
biochemical evidence of testosterone deficiency.
National and
International Guidelines are available which provide an evidence based
to the management of testosterone deficiency in men. The management of hypogonadism requires a careful diagnosis and replacement of
testosterone if indicated back to a consistently normal circulating
testosterone level at least in the mid-normal healthy range.
The primary indication for testosterone
therapy in men with diagnosed hypogonadism is sexual dysfunction.
Clinical trials have demonstrated that
symptoms of sexual function can
improve with testosterone replacement therapy. Studies also suggest that
there may be benefits on physical and psychological function as well.
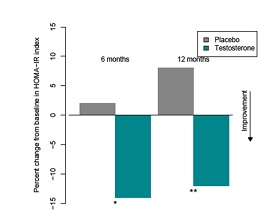
Clinical trials have reported that testosterone therapy
reduces insulin
resistance, body weight, waist circumference and some publications
suggest there is an improvement in HbA1c, lipid profile, reduction in
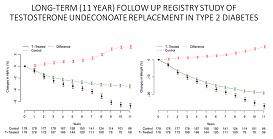
hepatic fat. A recent registry study has been published which
demonstrates a
gradual improvement in these parameters over several
years with some patients entering remission of their diabetes.
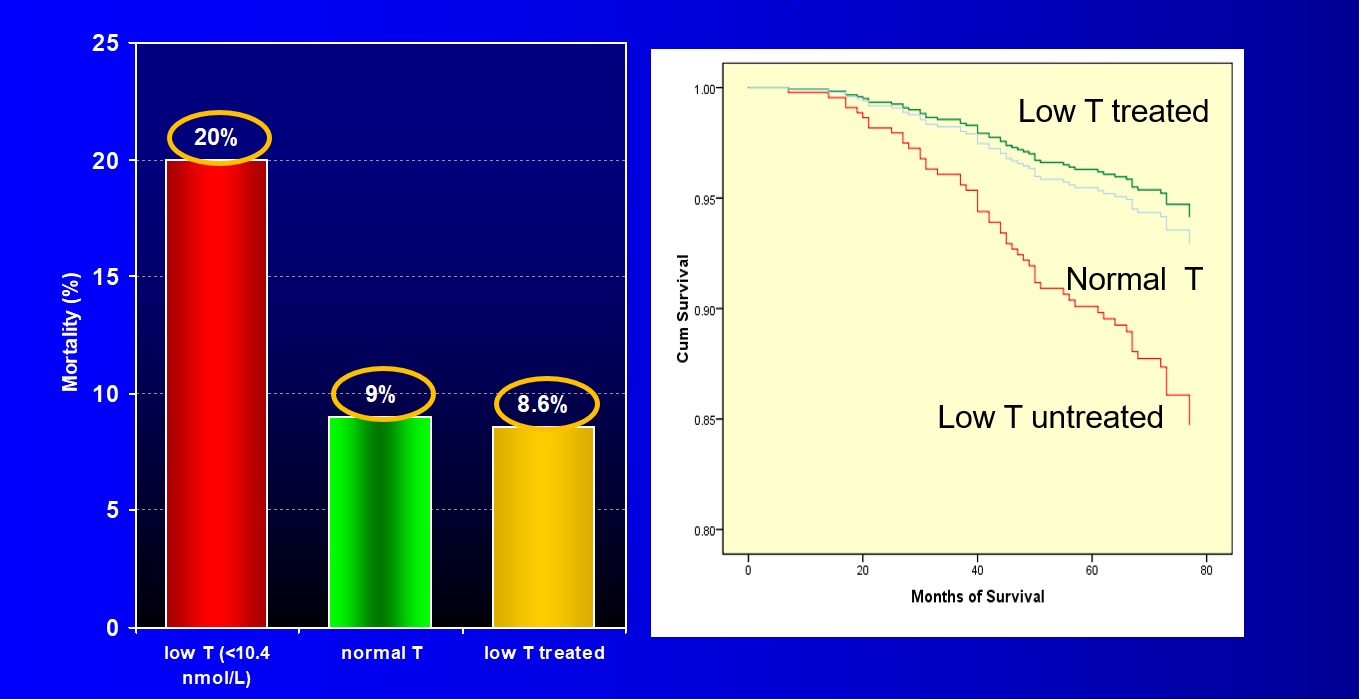
Epidemiological studies have found that testosterone deficiency is
associated with a
greater than two-fold increase in all-cause and
cardiovascular mortality in men with type 2 diabetes as well as other
populations. Reports also suggest that testosterone replacement in type
2 diabetes has a beneficial effect on survival. A recent large 2-year
study has reported that testosterone therapy with pre-diabetes and low
testosterone
reduces the proportion of men developing type 2 diabetes over and above
lifestyle changes.
Purpose of Audit
This audit sets out to help individual clinicians and to determine from
several centres the clinical effects and monitoring of testosterone
replacement therapy in men with type 2 diabetes and hypogonadism in real
world clinical practise in the short and longer-term. Data can also be
collected from men with hypogonadism where the decision by the patient
or clinician is not to treat.
Monitoring is essential to be sure there is a clinical improvement,
adequate replacement and to detect any adverse events. The haematocrit
and PSA should be assessed at baseline, 3,6 and 12 months and yearly
thereafter. Secondary polycythaemia can be managed in the majority of
cases (see guidelines). There is no evidence that testosterone
replacement causes the development of a new prostate carcinoma but may
after initiation unmask a mall unidentified occult cancer a few months
after initiation of treatment. The audit has a number of
objectives.
Collect data on-line or via paper forms
The Testosterone and Diabetes on-line audit tool is so easy to use that
live data entry in clinic is a real option to be considered. Otherwise
to facilitate data collection during clinics there are two paper forms
which exactly match the data that can be entered into the audit tool.
You can download and print these forms locally.
To download the forms to printout for use, use the following
links:
Download first visit data entry form
Download follow up visit data entry form
Non ABCD members
Non ABCD members are welcome to take part in the audit and will be given
access to the on-line audit tool when they register for the audit.
Analyse your own data
The tool will allow you to analyse the data of your own patients for
your own local interest; at the same time the data will automatically be
available for national analysis of anonymised data. Some videos showing
ways of analysing your own data are available through the ABCD YouTube
channel and some useful links to the videos can be found
here.
Acknowledgement of contributors
As we have done with previous audits all contributors will be
acknowledged in all papers and presentations from the audit data and
biggest contributors will be offered the possibility of being
co-authors.
Register to take part in the audit and access to the on-line
tool
To register for the audit and be given access to the on-line tool on the
ABCD website
click here.
Further
information
Further enquiries may be made to the ABCD nationwide audits
database administrator of the project,
Melissa Cull
|
Register for the Testosterone & Diabetes audit
Access the on-line tool
Audit objectives
Rationale for Audit Form
Helpful clinical tips and suggestions
Links to clinical guidelines on management of testosterone deficiency
AMS questionnaire
AMS evaluation form
Download first visit data entry form
Download follow up
visit data entry form
Papers, abstracts, presentations, posters from the audit
Further
information- contact us
Main ABCD homepage |

_in_Type_2%20Diabetes-thumb.jpg)